Key Highlights
Here are the key takeaways for your Thailand visa application:
- Your nationality determines if you need a visa, can enter visa-free, or get a visa on arrival.
- The Thailand visa system includes options for tourism, business, study, and long-term retirement.
- The visa application process can often be completed online through the e-Visa portal or at a Royal Thai Embassy.
- A tourist visa typically allows a 60-day stay, which may be extended for another 30 days.
- Understanding the specific visa requirements is essential for a successful application.
Introduction
Are you dreaming of a trip to the Land of Smiles? Thailand is a top destination for travelers, but navigating the visa system, established by the Thai government, can seem complicated. For most foreign nationals, securing a Thailand visa is a necessary first step. Understanding the visa requirements based on your travel plans and nationality is crucial for a hassle-free entry. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know, from different visa types to the application process, making your journey to Thailand much smoother.
Overview of Thailand Visa Requirements
Figuring out Thailand’s visa requirements starts with two key factors: your nationality and the purpose of your visit. Thanks to bilateral agreements, citizens of many countries can enter Thailand for a short period without a Thai visa. For longer stays or for citizens of other nations, an application is necessary.
The application process generally involves submitting documents to a Thai embassy or consulate, including the U.S. Consulate General in Chiang Mai. You’ll need a valid passport and other supporting paperwork. The exact entry rules depend on the type of visa you seek. We will explore who needs a visa and how to determine the right one for you.
Who Needs a Visa to Enter Thailand?
As a general rule, all foreign nationals who wish to enter Thailand must have a visa. However, there are important exceptions to this, including recommended vaccinations. The most common is the visa exemption scheme, which allows citizens from specific countries to enter for tourism for a set period without needing to apply for a visa in advance.
If your country, including Georgia, is not part of this scheme, you will need to secure a visa from a Royal Thai Embassy or Consulate before you travel. Whether you plan to work, study, or simply visit as a tourist for an extended time, a visa is mandatory.
Here’s a quick guide to who generally needs a visa:
- Individuals planning to stay longer than the visa exemption period allows.
- Foreign nationals intending to work or conduct business in Thailand.
- Travelers coming for purposes other than tourism, such as education or religious activities.
- Citizens of countries not included in the Visa Exemption or Visa on Arrival lists.
How to Determine Your Visa Necessity Based on Nationality
Your nationality is the single most important factor in determining your visa requirements for Thailand, including the requirement for a yellow fever vaccination if coming from a country at risk. The Thai authorities have different entry agreements with countries around the world, which dictates whether you can enter visa-free, need a Visa on Arrival (VOA), or must complete a full visa application beforehand.
Before making any travel plans, you should always check the latest rules for your specific passport. This information is available on the website of your nearest Thai embassy or consulate.
To give you an idea of how much this can vary, here is a simplified table showing different entry rules based on nationality, including for regions such as Hong Kong:
| Nationality | General Entry Rule for Tourism |
|---|---|
| United States | 60-day visa exemption |
| United Kingdom | 60-day visa exemption |
| India | Visa on Arrival (15 days) or e-Visa |
| China | Visa on Arrival (15 days) or e-Visa |
Types of Thailand Visas Explained
Thailand offers a diverse range of visas, including the destination Thailand visa, to accommodate every kind of visitor, from short-term tourists to long-term residents. Choosing the right type of visa is the first step in your visa application. Each category has its own specific purpose, validity period, and set of visa requirements that you must meet.
Whether you’re visiting for a holiday in France, exploring business opportunities, or planning to retire, there is a visa designed for your needs. Below, we’ll look at the most common options, including tourist visas, non-immigrant visas for work or study, and special long-term programs.
Thailand Tourist Visa Options
If you’re visiting Thailand, especially Phuket, purely for leisure or medical treatment, a Thailand tourist visa is what you need. The standard tourist visa, obtained from an embassy before you travel, typically grants a 60-day stay. This is a great option if you want more time to explore than the visa exemption period allows.
Remember that working on a tourist visa is strictly prohibited. After arriving in Thailand, you may be able to extend your stay once for an additional 30 days at a local immigration office for a fee.
Here are the primary options for tourists:
- Standard Tourist Visa: Apply at a Thai embassy for a 60-day stay.
- Visa Exemption Scheme: Enter without a visa for up to 60 days, depending on your nationality.
- Visa on Arrival (VOA): Eligible nationalities can get a 15-day visa upon arriving at specific entry points.
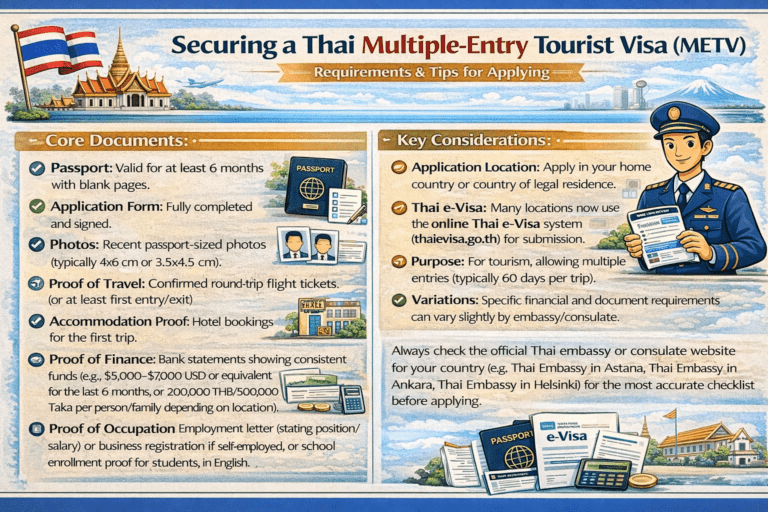
Non-Immigrant Visa Categories (Business, Student, Retirement)
For those planning to stay in Thailand for purposes other than tourism, a Non-Immigrant visa is required, which may involve the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. These visas cover a wide range of activities and are the gateway to obtaining a work permit or securing a long-term extension of stay within the country. Each category comes with its own unique visa requirements.
These visas are typically valid for an initial 90-day stay, during which you can apply for an extension or work permit related to your official duties. You must apply for the appropriate Non-Immigrant visa at an embassy before entering Thailand.
Common Non-Immigrant visa categories include:
- Non-Immigrant B Visa: For conducting business, seeking employment, or opening a company.
- Non-Immigrant ED Visa: For students enrolled in a recognized educational institution in Thailand.
- Non-Immigrant O-A Visa: For retirees over 50 years of age who meet the financial requirements.
Special Long-Term and Elite Visa Programs
Thailand also offers several premium long-term visa programs for individuals who wish to make the country their home for an extended period. These visas provide convenience and benefits that go beyond standard visa categories for holders, though they come with stricter financial or professional requirements. The Thai Immigration Bureau manages these special programs.
The Thailand Elite Visa, for example, is a long-term tourist visa offered through membership packages that cater to those interested in experiencing the luxury associated with the royal family, allowing stays from 5 to 20 years with a host of VIP perks. The Long-Term Resident (LTR) visa is another option aimed at wealthy individuals, retirees, and skilled professionals.
Key long-term visa programs include:
- Thailand Elite Visa: A privilege visa with membership tiers offering long stays and benefits like expedited immigration.
- Long-Term Resident (LTR) Visa: A 10-year visa for specific categories of foreigners, including investors and remote workers.
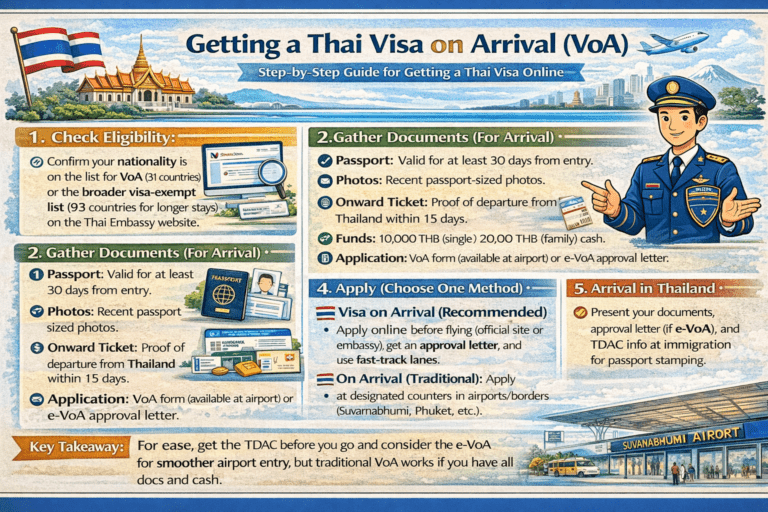
Thailand Visa on Arrival and e-Visa Programs
To simplify entry for travelers from certain countries, Thailand offers a Visa on Arrival (VOA) and an e-Visa program along with the Thailand Digital Arrival Card. The VOA allows you to obtain a 15-day visa right at the airport or land border checkpoint, saving you a trip to the embassy. It is a convenient but short-term solution.
The Thailand e-Visa program takes convenience a step further, allowing you to complete your entire visa application online before you travel. This modern system is faster and more accessible than the traditional process. We will now look into who is eligible for these programs and how they work.
Eligibility for the Visa on Arrival
The Visa on Arrival (VOA) is available to citizens of a select group of countries. If your nationality is on the eligible list, you can apply for a 15-day tourist visa upon reaching one of the 48 designated immigration checkpoints in Thailand, including major international airports.
To apply for a VOA, you will need a valid passport, a completed application form, a recent photo, and proof of onward travel. You must also pay a fee of 2,000 Thai Baht, and officials may ask for proof of accommodation and sufficient funds for your stay (10,000 THB per person).
Some nationalities eligible for the Visa on Arrival include:
- Bhutan
- China
- India
- Kazakhstan
- Saudi Arabia
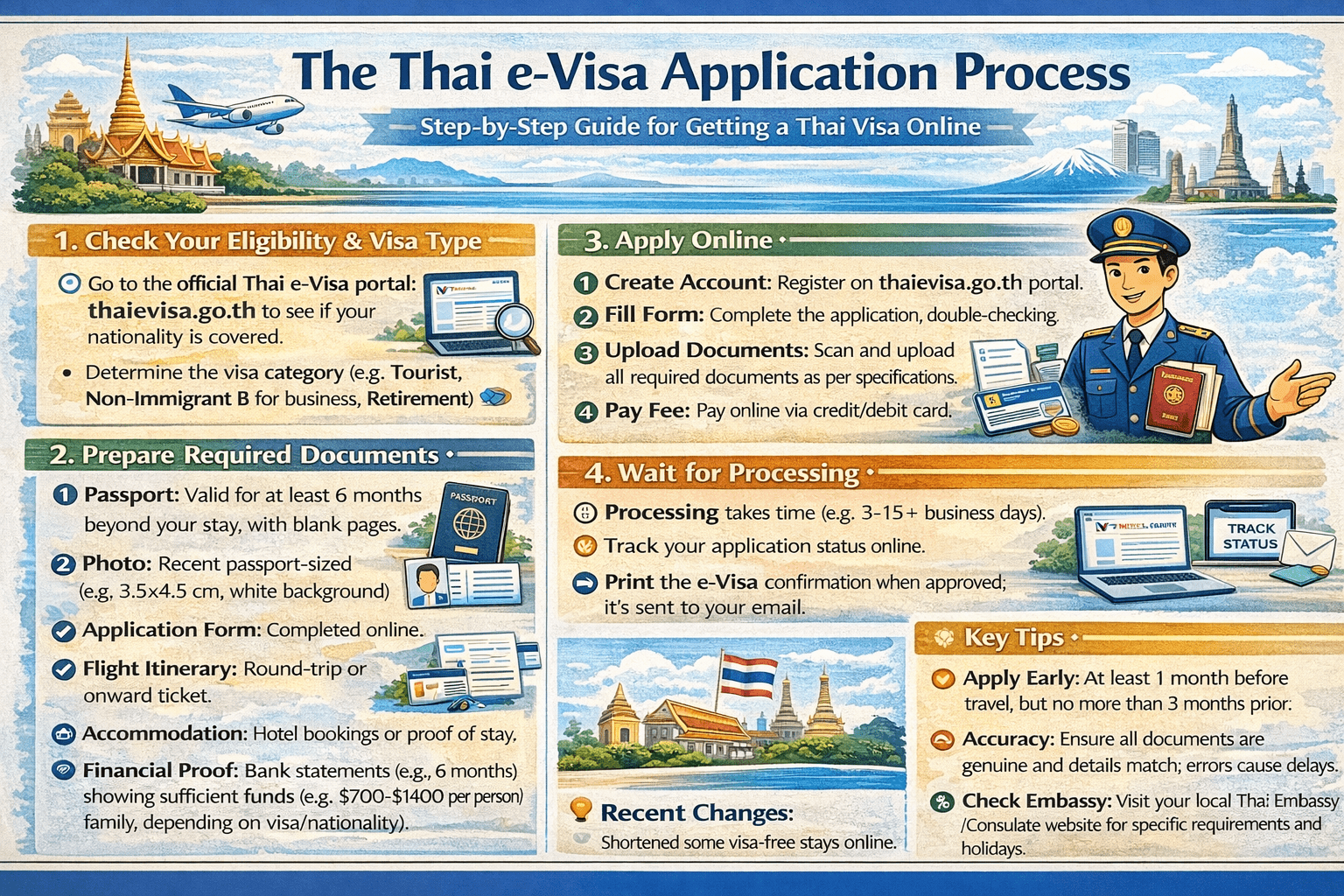
How to Apply for a Thailand e-Visa Online
Applying for a Thailand e-Visa is a straightforward online process that eliminates the need to visit a Thai embassy in person. This system allows you to submit your application and supporting documents from the comfort of your home. Since September, the process is designed to be faster and more efficient for travelers.
First, you need to visit the official Thailand e-Visa website at thaievisa.go.th. There, you will create an account, fill out the application form with your personal details and travel information, and upload digital copies of your passport and other required documents.
The steps for an e-Visa application are:
- Visit the official e-Visa website and create an account.
- Complete the online application form accurately.
- Upload all required documents, such as a passport scan and photo.
- Pay the visa fee online using a credit or debit card.
- Wait for the approval, which is sent via email.
Differences Between e-Visa and Traditional Visa Processes
The main difference between applying for an e-Visa and a traditional visa lies in the method of application and processing. The e-Visa offers a fully digital experience, while the traditional process requires a physical submission of documents to an embassy or consulate. This modernization makes the e-Visa a more convenient option for many travelers.
Thai authorities have streamlined the e-Visa system to reduce paperwork and shorten waiting times. With a traditional visa, you may need to mail your passport or make an appointment, which can take longer. The e-Visa, however, is processed online, and you receive a digital confirmation.
Key differences include:
- Application Method: The e-Visa is 100% online, while a traditional visa requires a visit to an embassy or submission by post.
- Processing Time: E-Visas are often processed faster, typically within 3-10 working days, whereas embassy processing can vary.
- Convenience: The e-Visa process can be completed from anywhere with an internet connection, offering greater flexibility.
Steps to Apply for a Thailand Visa from the United States
For citizens of the United States, planning travel to Thailand is relatively simple, but if you need a visa for a long stay or for work, you’ll need to follow a clear application process. Your first stop should be the official Royal Thai Embassy in Washington, D.C. website in the U.S. to find the most current guidelines and required forms.
Depending on the visa type, you may be able to apply through the online e-Visa portal or directly through the embassy. Preparing your documents correctly is key to a smooth process. Let’s break down the required documents and the steps to follow.
List of Required Application Documents
When applying for any Thailand visa, a set of standard required documents is necessary. Gathering these items before you start your application will save you time and prevent delays. While specific requirements can vary based on the visa type, some documents are universal.
Always check the checklist provided by the embassy or the e-Visa portal for the exact paperwork you need for traveling to the United Arab Emirates. For example, a business visa will require different supporting letters than a tourist visa. Make sure your passport is valid for at least six months from your intended date of entry.
Commonly required documents include:
- A completed visa application form.
- Your original passport with at least six months of validity.
- A recent passport-sized photograph.
- A copy of your flight itinerary.
- Proof of accommodation in Thailand.
- Evidence of sufficient funds for your trip.
Step-by-Step Online and Embassy Application Processes
Navigating the visa application process is easy once you know the steps. You can choose between an online application or a traditional submission through the embassy. The online process is generally recommended for its speed and convenience.
For an online application, you’ll use the official Thai e-Visa website. For an embassy application, you will need to download the forms from the Thai Ministry of Foreign Affairs embassy website, prepare physical copies of your documents, and submit them either in person or via mail as instructed.
Here’s a breakdown of the steps:
- Online Process:
- Go to the official Thai e-Visa website.
- Create an account and fill out the form.
- Upload digital copies of your documents and pay the fee.
- Embassy Process:
- Download and complete the application form.
- Gather all required physical documents.
- Submit your application packet to the designated Royal Thai Embassy.
Application Processing Times and Approval Expectations
Patience is key during the application process, as processing times for a Thailand visa can vary. The time it takes for an applicant to get their visa approved depends on the type of visa you are applying for and the workload at the specific Thai embassy or consulate. It is always wise to apply well in advance of your planned travel date.
Online e-Visa applications for Canada are often quicker than traditional embassy applications. However, during peak travel seasons or if your application requires extra scrutiny, delays can occur. Always factor in potential delays when planning your trip.
General processing time expectations are:
- e-Visa Application: Typically 3 to 10 business days.
- Embassy Application: Can range from a few days to several weeks, depending on the location.
- Visa on Arrival: Processed on the spot at the airport, which can take up to a few hours depending on queues.
Fees, Validity, and Extension Policies for Thailand Visas
Understanding the costs, how long your visa lasts, and your options for staying longer is an important part of your travel planning. The visa fee, validity period, and extension policies for a Thailand visa differ significantly based on the category you choose. Thai authorities set these rules, and they can change, so it’s good to be informed.
For instance, a single-entry tourist visa will have a different fee and validity than a multiple-entry business visa. Knowing these details helps you budget and plan your trip accurately. Let’s look closer at the current fees and extension options available.
Current Visa Fees by Category and Duration
The visa fee for a Thailand visa is determined by its category and the number of entries it permits. Additionally, some countries may benefit from visa fee exemption agreements with Thailand. Fees are typically paid in the local currency of the country where you apply, or in Thai Baht (THB) if applying within Thailand for an extension or on arrival.
These fees are non-refundable, even if your application is rejected. The cost can range from a modest amount for a single-entry tourist visa to a more substantial sum for long-term or specialized visas. Always confirm the current fee with the embassy before submitting your application.
Here is an example of common visa-related fees:
| Visa/Service Type | Typical Fee (in Thai Baht) |
|---|---|
| Visa on Arrival | 2,000 THB |
| Tourist Visa Extension | 1,900 THB |
| e-Visa Fee | Varies by nationality and visa type |
Extending Your Stay or Changing Visa Types in Thailand
What if you fall in love with Thailand and want to stay longer? Fortunately, extending your stay is often possible. If you entered on a tourist visa or under the visa exemption scheme, you can typically apply for a 30-day extension at any local immigration office in Thailand.
Changing your visa type, for instance from a tourist visa to a non-immigrant visa, is a more complex process. It usually requires a new visa application and may involve leaving the country to apply at an embassy abroad. It’s crucial to follow the procedures set by Thai authorities to avoid overstaying.
Here’s what you need to know about extensions:
- Apply for an extension before your current permission to stay expires.
- Visit a Thai Immigration Bureau office with your passport and required forms.
- Pay the extension fee, which is currently 1,900 THB.
- Changing visa types often requires a new application from outside Thailand.
Conclusion
In conclusion, navigating the visa application process for Thailand can seem daunting, but with the right information at your fingertips, it becomes manageable. Understanding the various visa types, requirements, and application procedures ensures that you are well-prepared for your journey. Whether you’re planning a short vacation or a long-term stay, ensuring you have the correct visa will allow you to fully enjoy all that Thailand has to offer. If you’re ready to take the next step in your travel plans, don’t hesitate to reach out for assistance. A smooth visa application process is just a consultation away!
Frequently Asked Questions
What should I do if my Thailand visa application is rejected?
If your Thailand visa application is rejected, first review the reason provided by the embassy. You can then correct any issues with your application, such as missing documents, and reapply. If the reason is unclear, you may be able to contact the embassy for more information before submitting a new application.
Where can I find the official Thailand visa application website?
You can find the official Thailand e-Visa application website at thaievisa.go.th. This is the official government portal for submitting your application form and documents online. For traditional applications or specific information about Bangkok, visit the official website of the Royal Thai Embassy or Consulate in your country of residence.
Are there specific requirements for long-term visas to Thailand?
Yes, long-term visas for Thailand have specific requirements. For instance, a retirement visa requires you to be over 50 and meet financial criteria. The LTR and Elite Visa programs also have significant financial or professional requirements, and it’s beneficial to communicate in English with the embassy for your desired long-term visa. Always check the detailed requirements.